Manufacturing existed before the emergence of modern humans approximately 200,000 years ago. Humans have been industrious since the dawn of time, with the earliest stone tools being over two million years old. As time passed, technology permitted the creation of pottery kilns that later evolved to allow copper smelting. During the Bronze Age, people started making more intricate objects, which also facilitated the development of shipbuilding. Then, the Iron Age replaced bronze with steel and iron. Civilisations began to develop, and the Mesopotamians created the wheel, while the Ancient Egyptians mass-produced pottery for export in the Mediterranean.
The Medieval and Early Modern Period innovations saw the rise of papermaking, blast furnaces in metal production, and the stocking frame for textiles, which increased the number of knots per minute from one hundred to one thousand. The Impact of the Industrial Revolution can still be observed today, as, during this time, manufacturing moved from crafting and handmade production to a system that primarily uses machines. The chemical industry, hydropower, mechanised textile production, assembly lines, agricultural machinery and the widespread use of electricity were all established during this period.
Electrification created today’s mass production, and although it might seem that all goals were already achieved in the manufacturing sector, that’s far from the truth. In fact, innovations continue to play an important part, as many eagerly await to see how the processes will change in the future.
Injection moulding
The injection moulding process is a complex and versatile manufacturing method that permits the creation of objects of all shapes and sizes, which can be employed for many purposes. Molten plastic materials are injected into a mould, after which they solidify during the cooling process. This straightforward method is suitable for creating a wide range of products, from simple to more intricate, and plays a prominent role in plastic processing.
There are several types of items that can be created this way. Injection moulding of large plastic products such as air-conditioning systems and electronics see daily use. Items used in infrastructure and leisure, from dashboards to folding furniture and children’s playground slides, are all created via this type of injection moulding.
Structural foam moulding has led to revolutionary changes in the design of vehicle roofs, skis and medical equipment. Its main advantages are that this process reduces the risk of deformations and permits differing thickness options for the walls, allowing for increased product versatility. As such, there’s ample room for creativity and development when it comes to design choices compared to high-pressure moulding.
Artificial intelligence
Arguably the most controversial development of recent years, artificial intelligence has created a polarised debate among politicians, scientists and members of the general public as to whether its potential risks and irregularities outweigh the benefits. Artificial intelligence mimics human intelligence by using algorithms to learn from its mistakes and improve how it performs tasks. The system relies on natural language processing and deep learning to adjust to new input and improve efficiency.
Because of its far-reaching abilities, artificial intelligence can perform a wide range of tasks across different industry sectors. AI can be used as part of more accurate analysis and predictions, delivering more accurate figures concerning the use of materials and production demands. Moreover, manufacturers can use it to handle all shipping areas, from basic management to complex scheduling issues.
Data collection also enables businesses to be more efficient as entrepreneurs learn what they need to do to improve their services. Machines can also be equipped with the necessary technology that allows them to self-diagnose and predict maintenance needs with a sizable degree of accuracy. However, some have expressed concerns about what they believe could signal trouble for employees and customers, such as unemployment, data security issues, inserted biases, lack of transparency and misinformation.
3D printing
Not long ago, the concept of 3D printing may have sounded like something that belongs in a science fiction book. But it’s real and used in manufacturing nowadays. Material is settled and solidified using computer control, generally in a layer-by-layer pattern. All types of materials can be used, from plastic to powders, metals and even foods.
The main advantage of 3D printing is that it produces far less waste than traditional manufacturing, which is helpful for businesses looking to improve their waste management practices and create less rubbish. If your company is seeking to become zero waste, 3D printing might be the answer.
Even if it isn’t used to mass-produce new objects, it can still assemble prototypes. Developers can minimise the time it takes to settle down design to start production, creating seamless processes and ensuring smoother business functioning.
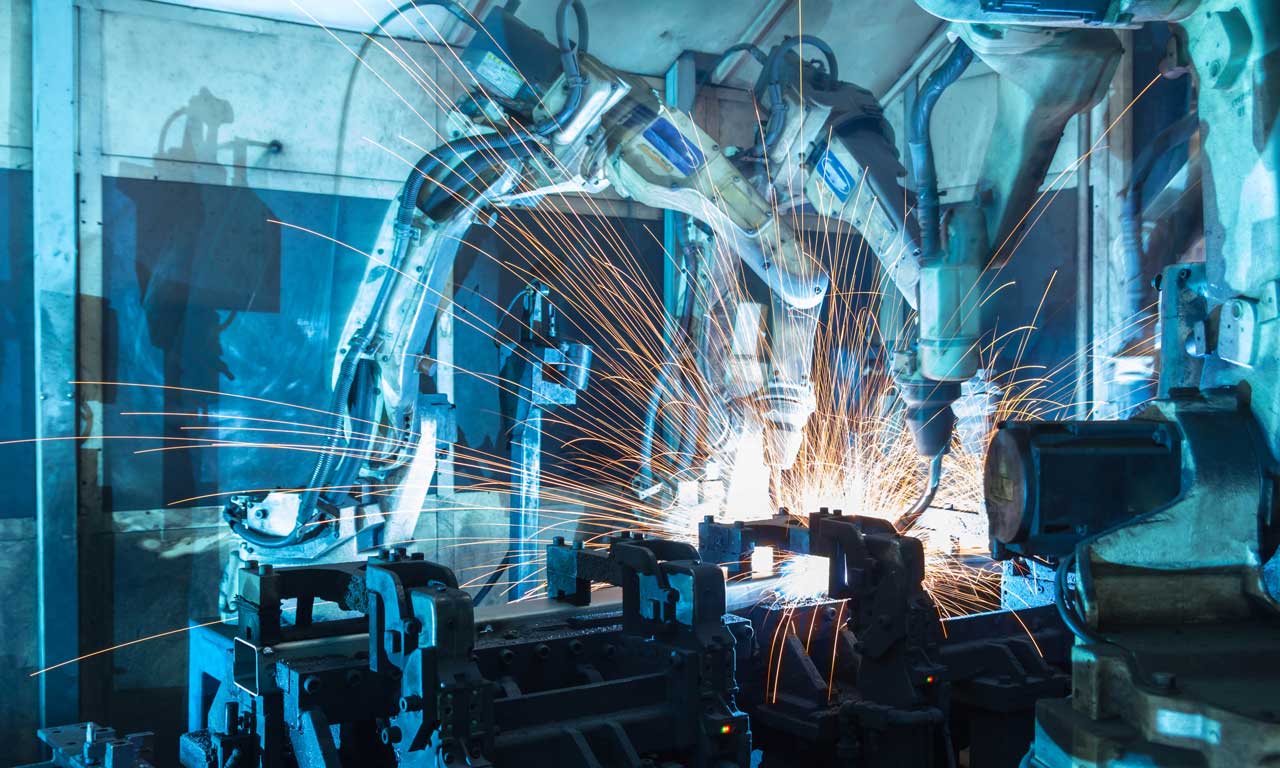
Robotics
The use of robots in the industry sector is nothing new. Even small businesses have begun using them recently, so they’re no longer the sole domain of large corporations. Now, with the advent of artificial intelligence, it’s very likely that robotics will further develop as well. Using machinery means that repetitive tasks can be automated more efficiently so that human manufacturers can focus on more complex and productive jobs.
The robots require no breaks and can perform repetitive tasks without the risk of errors. They can be used for a wide area of assignments, from painting to assembling, and their features enable businesses to be more efficient and precise in delivering their products.
Industrial IoT
The Internet of Things is the technology that allows several devices and gadgets to be connected to the Internet in order to collect information and deliver a better user experience. The concept of smart homes is the most well-known example of this category. However, it is known as the Industrial Internet of Things when applied to the manufacturing environment.
Like the traditional IoT, this system combines cybersecurity with advanced robotics, machine-to-machine, edge computing, mobile tech and big data analytics. The aim is to send more accurate reports and ensure faster data collection for entire facilities.
Technology continues to evolve, continuing the development of the manufacturing sector. As time progressed, the objects humanity created became increasingly more complex, but it all started millions of years ago with rudimentary tools. Production processes have come a long way since then.
Thanks for reading this article. If you're new here, why don't you subscribe for regular updates via RSS feed or via email. You can also subscribe by following @techsling on Twitter or becoming our fan on Facebook. Thanks for visiting!