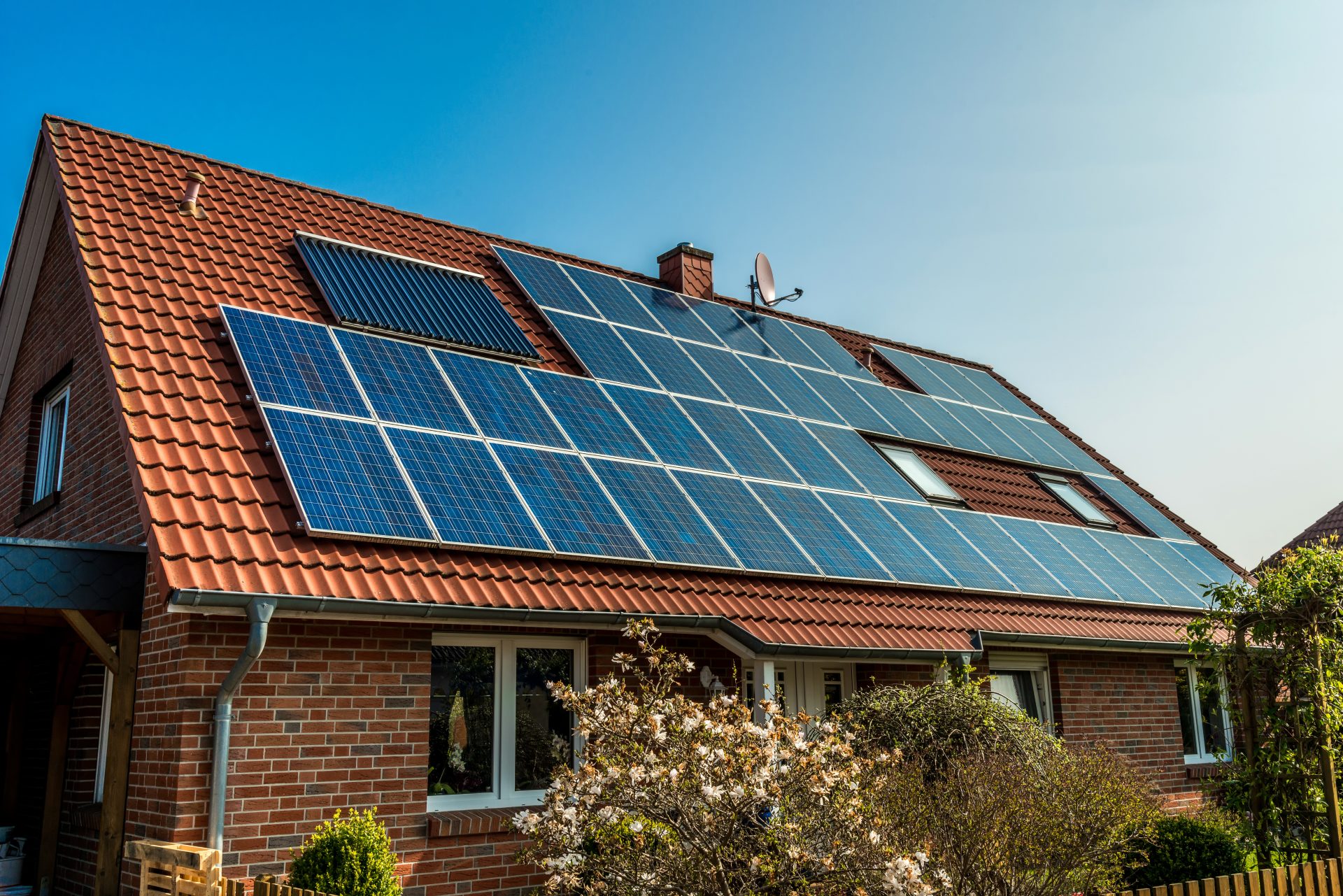
Using renewable sources of energy, including solar power, to generate low-carbon electric power was once considered highly uneconomical. Today, rapidly falling costs of wind and solar technologies are boosting global renewable energy capacity. The April World Economic Outlook points towards the largest price declines in low-carbon energy sources from 2009 to 2017, with the price of solar panels has dropped 76% during this period, making them a highly competitive alternative to fossil fuels, says an article by the International Monetary Fund.
On a household level, this spells good news, since the increased use of solar panels to generate electricity will not only reduce greenhouse gas emissions but also reduce water pollution, according to an article by Suntuity Solar. It, therefore, comes as no surprise that countries all across the world have launched their own programs to promote the use of this infinite source of clean energy.
Tesla’s High Solar Ambitions
2019 is the year when the use of coal power was surpassed in the US by renewable sources of energy. An IEEFA report states that the renewable energy sector generated more electricity than coal during April 2019. Coal consumption declined to its lowest levels in 2018, since 1979, according to a report on CNN. Joining this revolution is tech-giant Tesla, which slashed its solar panel costs below the national average. The company has standardized systems and is facilitating online-orders for solar panels by customers.
Egypt Will Launch a Fully Operational Solar Park by mid-2019
Funded by the World Bank, Egypt’s giant 1.6-gigawatt solar park will be fully operational in 2019, according to a report by ET Energy World.com. This $2 billion project will be able to meet 20% of the country’s energy needs by 2022 and up to 40% of its needs by 2035. Egypt is known for its vast access to solar energy, which the country gets in abundant supply. Some parts of this park are already functional, while many others are in their testing phase. This will also open avenues for wide-scale private sector investments in the renewable energy industry.
South Africa’s Solar Power Revolution
A major energy crisis hit the nation of South Africa, bringing the national electricity grid to the point of collapse, following a decade of mismanagement and corruption. But the country’s younger generation is leveraging its vast access to sunshine, 2,500 hours a year on average, through the solar power plant, called Pele, located in Touws River, near Cape Town. The company that has given residents a 5% stake in the ownership of the power plant, generates enough energy to serve 36,000 households in the area, according to a report on CBS News. This will be a huge benefit to the country’s farming industry, especially the vineyards and vast fruit orchards, which have suffered due to large scale power outages in the nation in the last few years.
India’s Solar Capacity is Now 30GW
Solar installations in India have reached a milestone figure of 30GW, according to the country’s Solar Project Tracker report, published on Mercom India. With this, 30% of the solar installation goal of 100GW by 2022, set by the current government, has been achieved. The country continues to see a surge in its renewables capacity, at about 22.3% of the total power capacity mix in 2018-19 from the previous 20.3% share reported in 2017-18.
The global renewable energy sector has remained stable in 2018, despite uncertainties regarding new tariffs and tax policies, and the Brexit negotiations. In 2019 too, tax policies, like the new lower US federal tax credits scheme, will compel developers to speed up their solar projects.
Around the world, the ill effects of climate change have altered popular consumer sentiment in favour of renewable sources of energy. The time seems ripe for a global solar energy revolution.
Marcelo Fincher is a blogger & writer on technology related topics with years of experience in studying technological advancements. In his spare time, Marcelo likes to read books and take a walk on the beach.