Just 20 years ago, fingerprint scanners, facial recognition software, and voice-activated devices would have been considered “future-tech,” denoting innovations that aren’t quite science fiction anymore, but still aren’t quite reality either. Nevertheless, as tangential technologies such as the IoT have grown, so have security issues related to them.
Because of the rise of cybercrime and social engineering, traditional passwords aren’t always enough to thwart attackers anymore — but, fortunately, biometric technology has become more potent in recent years, and its deployment as a security solution has been met with enthusiasm. Here are just a couple of ways that we’ve begun using biometric technology in the modern world.
Mobile Devices
In 2013, when Apple announced the release of its then-newest phone, most of us held our breath. How would the iPhone 5S differ from the 5? It was faster, cleaner, took better photos — but it was also the first phone with the ability to identify users by capacitive fingerprint scan.
By storing up to five unique fingerprints, a person could both unlock a phone and make purchases with their Apple ID using the Touch ID feature. Touch ID will misread a finger only 1 in 50,000 times which is significant, given the 1 in 10,000 likelihood that a four digit password will be guessed.
Apple isn’t alone — since then, plenty of other manufacturers have added fingerprint sensor and other biometric tech to their phone designs. The real potential, though, is in the ability to utilize this mobile technology as a biometric payment system, which experts expect to play a major role in the future of business. This increased online security by way of a mobile device will likely encourage even more online purchases on the go — a great thing for economy.
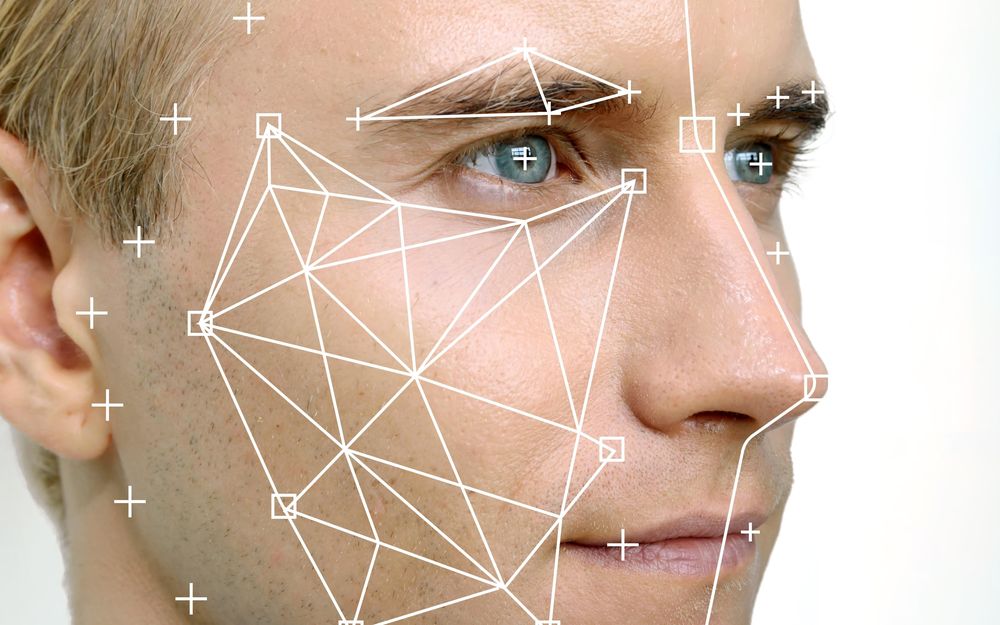
Fingerprint biometrics on phones are almost old news by this point. What’s really making waves with Apple smartphones nowadays is Face ID, a face unlock facial recognition system that other phone developers, including Huawei, are looking to emulate in their own phones. In another five years, you can bet that most phones with front-facing cameras will have some kind of facial recognition technology.
Time and Attendance Tracking
A 2013 Replicon survey of 432 professionals responsible for tracking employee time showed that 96 percent of employees make time tracking mistakes. Even worse, buddy-punching, which is believed to cost U.S. companies nearly $400 billion per year, can be a huge problem as well.
The American Payroll Association estimates that the use of punch cards for time management in business situations tacks on an extra 6 percent in payroll expenses every year — significant numbers if you’re a large business or one just starting up.
Fortunately, biometric technologies are now being utilized to prevent losses related to buddy-punching, tabulation errors, etc. They’re also being used in workplaces in which high end items are stored — car dealerships, IT departments, cash and control rooms — to monitor who is able to access such valuable assets.
Time and attendance software programs that utilize biometric technologies promise to increase profit by decreasing wasted time, keeping businesses more secure, and providing employers and employees with a simple way to manage time.
Keyless Entry and Public Safety
A logical extension of biometric fingerprint technology is keyless identity management and access control systems to help provide schools, businesses, and other public and private places with additional safety features. By scanning each student and/or staff fingerprint for access control, administrators can gain real-time visibility into who is “on-campus” within seconds, thereby increasing their own security measures.
Another way that biometrics are currently being used in public is in conjunction with facial-recognition technology, not unlike Apple’s Face ID.
“Advanced camera and sensor technology is now available that can support police officers in their investigations,” explain the experts at the University of Cincinnati. “…facial recognition technology works by identifying the detailed facial measurements of an individual, capturing details in just a fraction of a second. Then, this information is compared to other scanned facial data in a database to check for matches. Facial recognition is still a young technology, and there is much conversation about its use, not just in a policing setting, but in other environments as well – retail stores, amusements parks, city streets, etc.”
Using these biometric systems, finger or facial scans can be used to track specific student, staff, or visitor locations, as well as their specific entrances and exits. These records, complete with timestamps, can be accessed at any time.
Downsides of Biometrics
Biometric technology, while able to offer many solutions to today’s problem, is not perfect. There are, in fact, quite a few concerns related to its use.
One must look no further than the Equifax hack of 2017, in which personal identifying information of millions of adults was compromised. It wasn’t just passwords either, but things like social security numbers, data that can’t just be “changed” on a whim.
If biometric data were to be hacked, we’d be looking at a similar situation. For biometrics to work in the future, firms backing the technology need to make sure that they’re treating that data in the same way that HIPAA-compliant firms treat data, including de-identification measures:
“The de-identification process typically involves removing any and all information from medical data that could potentially be used to identify the patient,” writes Maryville University’s experts. “Identifying data can include names, addresses and geographical data, phone numbers, email addresses, Social Security numbers, account numbers, vehicle identification information, biometric identifiers, and anything else that keeps the data from being truly anonymous.”
So, on the one hand, biometrics look highly appealing as a security prospect — on the other, it’s still got its downsides to work through. Nevertheless, as technology continues to provide us with new and better solutions to our everyday problems, we can look forward to business and schools that operate more concisely and safely. Biometric technology is just the start.
Andy is a tech writer from Boise, ID. He enjoys wine, beer, and being drunk--but unfortunately is on a health-conscious kick at the moment, meaning he'll be drinking neither any time soon. Follow him on Twitter @AndyO_TheHammer

1 Comment
Leave a Reply
Cancel reply
Leave a Reply
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed.












































































































































































Karen Ching
September 16, 2018 at 4:08 pm
I totally agree. Biometrics has it’s downsides too, just like any other technological advancements made. But we also can’t deny how it is being so helpful for us, especially in the corporate world. And as said in the article, we can look forward to better innovations as technology continues to provide us better solutions everyday 🙂